算法 - (二叉树)
二叉树(Binary tree)是树形结构的一个重要类型。许多实际问题抽象出来的数据结构往往是二叉树形式,即使是一般的树也能简单地转换为二叉树,而且二叉树的存储结构及其算法都较为简单,因此二叉树显得特别重要。以下会以几道 LeetCode 巩固自己的基础
生成一个二叉树
二叉树结构
type TreeNode struct {
Val int
Left *TreeNode
Right *TreeNode
}二叉树的工厂模式
- 创建节点、打印节点、设置节点
// 创建节点
func CreateNode(val int) (node *TreeNode) {
return &TreeNode{val,nil,nil}
}
// 打印节点
func (node *TreeNode) Print() {
fmt.Print(node.Val)
}
// 设置节点
func (node *TreeNode) SetVal(val int) {
node.Val = val
}- 添加节点
func (node *TreeNode) Add(val int) {
if val < node.Val {
if node.Left == nil {
node.Left = CreateNode(val)
}else {
node.Left.Add(val)
}
}else {
if node.Right == nil {
node.Right = CreateNode(val)
}else {
node.Right.Add(val)
}
}
}二叉树的遍历
经典的方法有三种,前序遍历、中序遍历和后序遍历。这三种遍历都是 DFS 深度优先遍历算法
其中,前、中、后序,表示的是节点与它的左右子树节点遍历打印的先后顺序。动画演示
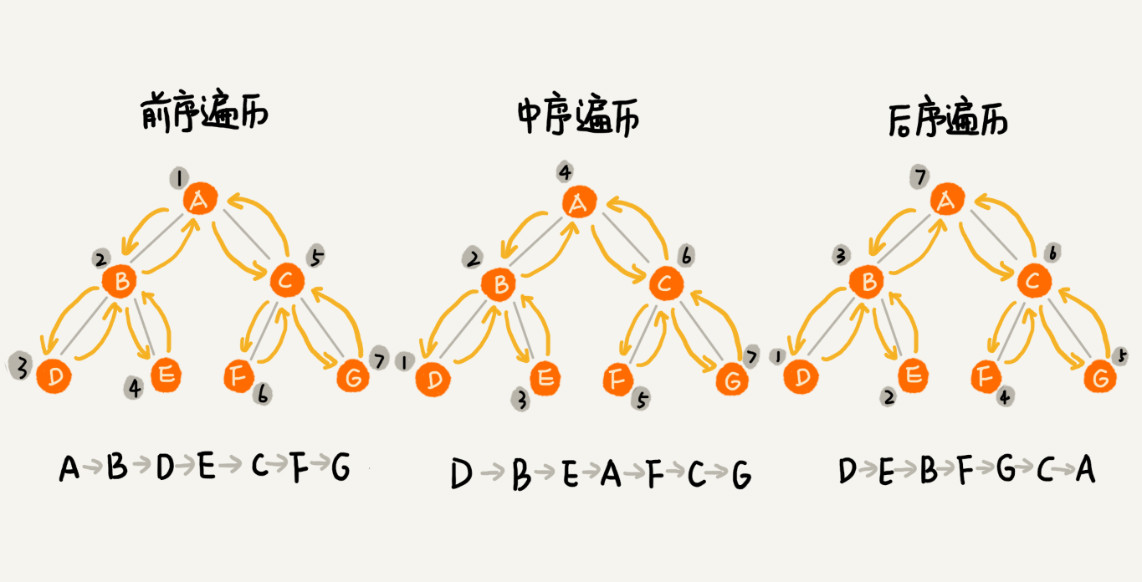
前序遍历是指,对于树中的任意节点来说,先打印这个节点,然后再打印它的左子树,最后打印它的右子树。
中序遍历是指,对于树中的任意节点来说,先打印它的左子树,然后再打印它本身,最后打印它的右子树。
后序遍历是指,对于树中的任意节点来说,先打印它的左子树,然后再打印它的右子树,最后打印这个节点本身。
前序遍历的递推公式:
preOrder(r) = print r->preOrder(r->left)->preOrder(r->right)
中序遍历的递推公式:(中序排列结果为有序数组)
inOrder(r) = inOrder(r->left)->print r->inOrder(r->right)
后序遍历的递推公式:
postOrder(r) = postOrder(r->left)->postOrder(r->right)->print rLC 二叉树 前序遍历 (DFS)
例题链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/data-structure-binary-tree/xeywh5/
func preorderTraversal(root *TreeNode) []int {
if root == nil {
return []int{}
}
var list []int
list = append(list, root.Val)
resLeft := preorderTraversal(root.Left)
resRight := preorderTraversal(root.Right)
return append(list, append(resLeft, resRight...)...)
}
func main() {
treeRoot := CreateNode(0)
treeRoot.Add(-2)
treeRoot.Add(3)
treeRoot.Add(8)
treeRoot.Add(4)
treeRoot.Add(5)
treeRoot.Add(-2)
treeRoot.Add(1)
treeRoot.Add(2)
fmt.Println(preorderTraversal(treeRoot))
}
// 打印
[0 -2 -2 3 1 2 8 4 5]LC 二叉树 中序遍历(DFS)
func inorderTraversal(root *TreeNode) []int {
if root == nil {
return []int{}
}
var list []int
list = append(list, root.Val)
resLeft := inorderTraversal(root.Left)
resRight := inorderTraversal(root.Right)
return append(resLeft,append(list,...), resRight...)
}
// 打印
[-2 -2 0 1 2 3 4 5 8]LC 二叉树 后序遍历(DFS)
func postorderTraversal(root *TreeNode) []int {
if root == nil {
return []int{}
}
var list []int
list = append(list, root.Val)
resLeft := postorderTraversal(root.Left)
resRight := postorderTraversal(root.Right)
return append(resLeft, append(resRight,list...)...)
}
// 打印
[0 -2 -2 3 1 2 8 4 5]二叉树的层次遍历(BFS广度优先遍历)
例题链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/data-structure-binary-tree/xefh1i/
题解: 创建一个先进先出的队列,从最顶层的节点依次加入节点,并遍历该层,每遍历该层的一个节点,把该层的子节点加入的队列的后面,这样就可以实现层次遍历,如果要蛇形遍历也是一个道理。
func levelOrder(root *TreeNode) [][]int {
var level [][]int
if root == nil {
return level
}
queue := list.New() // 一个先进先出的队列,所有的元素需要依次进队
queue.PushFront(root)
for queue.Len() > 0 {
var curLevel []int
curLevelLength := queue.Len()
for i := 0; i < curLevelLength; i++ {
// 从尾部抽出上一层,新一层追加到队前
node := queue.Remove(queue.Back()).(*TreeNode)
curLevel = append(curLevel, node.Val)
if node.Right != nil { // 下一层遍历做准备, 把当前节点的子节点都加进去
queue.PushFront(node.Right)
}
if node.Left != nil {
queue.PushFront(node.Left)
}
}
level = append(level, curLevel)
}
return level
}LeetCode
No.100 相同的树
思路:相同的二叉树肯定所有节点都相同,通过递归的方式对比。首先如果都是 nil, 则返回true, 再接着任意一个不是nil 则返回false, 再接着一个递归完成
func isSameTree(p *TreeNode, q *TreeNode) bool {
if p == nil && q == nil {
return true
}
if p == nil {
return false
}
if q == nil {
return false
}
return q.Val == p.Val && isSameTree(p.Left, q.Left) && isSameTree(p.Right, q.Right)
}
func isSameTree(p *TreeNode, q *TreeNode) bool {
if (p == nil && q != nil) || (p != nil && q == nil) {
return false
}
if p == nil && q == nil {
return true
}
return p.Val == q.Val && isSameTree(p.Left, q.Left) && isSameTree(p.Right, q.Right)
}No.101 对称二叉树
思路:对称二叉树?是不是和上面的题目比较像。其实就是将 root 节点的右子树和左子树做一次类似 isSameTree 这样的操作即可。但是注意,这是镜像关系,所以将 isSameTree 递归的时候填写p的左子树和q的右子树。同理相反。
func isSameTree(p *TreeNode, q *TreeNode) bool {
if p == nil || q == nil {
return p == q
}
if q.Val == p.Val {
return isSameTree(p.Left,q.Right) && isSameTree(p.Right,q.Left)
}else {
return false
}
}
func isSymmetric(root *TreeNode) bool {
if root == nil {
return true
}
return isSameTree(root.Left, root.Right)
}No.104 二叉树的最大深度
- 链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/
- 思路:一个非常简单的递归解决的问题。
func maxDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
return int(math.Max(float64(maxDepth(root.Left)),float64(maxDepth(root.Right))) + 1)
}No.108 将有序数组转为二叉搜索树
- 链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/convert-sorted-array-to-binary-search-tree/
- 思路:高度平衡 二叉树是一棵满足「每个节点的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1 」的二叉树。想要生成一个平衡的二叉树,当然是左子树的元素个数尽可能的等于右子树的元素个数。那么有序数组的中间元素一定要插入到二叉树的顶点,同理递归。
func sortedArrayToBST(nums []int) *TreeNode {
return helper(nums, 0, len(nums) - 1)
}
func helper(nums []int, left, right int) *TreeNode {
if left > right {
return nil
}
mid := (left + right) / 2
leftNode = helper(nums, left, mid - 1)
rightNode = helper(nums, mid + 1, right)
return &TreeNode{Val: nums[mid], Left: leftNode, Right: rightNode}
}No.110 判断平衡二叉树
- 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/ping-heng-er-cha-shu-lcof/
- 思路:平衡二叉树的判断方式即某二叉树中任意节点的左右子树的深度相差不超过1,那么它就是一棵平衡二叉树。 而一个数的高度为左子树和右子树中最高的。即只要比对左右子树的高度即可判断是否为平衡二叉树。
// 获取树的高度
func getTreeDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
return int(math.Max(float64(getTreeDepth(root.Left)), float64(getTreeDepth(root.Right)))) + 1
}
func isBalanced(root *TreeNode) bool {
if root == nil {
return true
}
left := getTreeDepth(root.Left)
right := getTreeDepth(root.Right)
// 判断左子树和右子树的绝对差值小于1 且 左子树 和 右子树 也满足平衡
if math.Abs(float64(left) - float64(right)) <= 1 && isBalanced(root.Left) && isBalanced(root.Right) {
return true
}
return false
}No.111 二叉树的最小深度
- 链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree/
- 思路:找到 Left 和 Right 节点均为 nil 的即为最小深度
func min(a,b int) int {
if a < b {
return a
}
return b
}
func minDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
if root.Right == nil {
return 1 + minDepth(root.Left)
}
if root.Left == nil {
return 1 + minDepth(root.Right)
}
return min(minDepth(root.Left), minDepth(root.Right))+1
}No.112 路径总和
- 链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum/
- 思路:这种类似与 二叉树的深度遍历DFS肯定是要用到递归了。。
func hasPathSum(root *TreeNode, sum int) bool {
if root == nil {
return false
}
if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil {
return sum == root.Val
}
return hasPathSum(root.Left, sum-root.Val) || hasPathSum(root.Right, sum-root.Val)
}No.124 二叉树中的最大路径和
二叉树中的 路径 被定义为一条节点序列,序列中每对相邻节点之间都存在一条边。同一个节点在一条路径序列中 至多出现一次 。该路径 至少包含一个 节点,且不一定经过根节点。
路径和 是路径中各节点值的总和。
给你一个二叉树的根节点
root,返回其 最大路径和 。
// TreeNode 定义了二叉树节点
type TreeNode struct {
Val int
Left *TreeNode
Right *TreeNode
}
// 全局变量,用于存储最大路径和
var max int
func maxPathSum(root *TreeNode) int {
// 初始化最大值为最小可能值
max = math.MinInt64
maxPathSumHelper(root)
return max
}
// 辅助函数,返回以当前节点为起点的最大单边路径和
func maxPathSumHelper(node *TreeNode) int {
// 1. 基准情况
if node == nil {
return 0
}
// 2. 递归计算左右子树的最大单边路径和
// 使用 max(0, ...) 避免负值影响
leftMax := maxPathSumHelper(node.Left)
if leftMax < 0 {
leftMax = 0
}
rightMax := maxPathSumHelper(node.Right)
if rightMax < 0 {
rightMax = 0
}
// 3. 计算经过当前节点的最大路径和,并更新全局最大值
// 这条路径可以包含左子树、右子树和当前节点
// 这里的 leftMax 和 rightMax 已经是正数或 0
currentPathSum := node.Val + leftMax + rightMax
if currentPathSum > max {
max = currentPathSum
}
// 4. 返回当前节点的最大单边路径和,供父节点使用
// 父节点只能选择左子树或右子树中的一条路径
if leftMax > rightMax {
return node.Val + leftMax
}
return node.Val + rightMax
}No.226 翻转二叉树
思路:老样子,肯定是一道递归题,我们只需要思考当前一层该如何计算即可,假设
1 2 3这样一颗树,那么翻转就是
left := root.Leftright := root.Right最后再root.Left = right root.Right = left即可。很显然,左子数将重复进行上述递归操作,同理右子树。func invertTree(root *TreeNode) *TreeNode { if root == nil { return nil } left := invertTree(root.Left) right := invertTree(root.Right) root.Left = right root.Right = left return root }
No.235 二叉搜索树的公共祖先
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-search-tree/
思路:
通过搜索的方式查找节点,并记录所有节点,查到2个点之后,比对两个查找链路上的最后一个公共节点即可
判断P,Q 两个节点如果在都小于root,则公共节点一定是在左子树,反之同理。
func lowestCommonAncestor(root, p, q *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
if root == nil || root == q || root == p {
return root
}
if p.Val <= root.Val && q.Val <= root.Val { //p和q都小于root,公共祖先节点一定在root的左边
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.Left,p,q)
}
if p.Val >= root.Val && q.Val >= root.Val { //p和q都大于root,公共祖先节点一定在root的右边
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.Right,p,q)
}
return root
}No.404 左叶子之和
- 链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/sum-of-left-leaves/
- 思路:递归!!刚开始理解错了,只要是左子树上的值就加起来,导致计算的数值偏大。详细看了题解,除了是左子树,还得是左子节点。
// 如果左子树上的节点全部计算,则是下面的解法,但不是本题想要的结果
func sumOfLeftLeaves(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
var left int
if root.Left != nil {
left = root.Left.Val
}
return left + sumOfLeftLeaves(root.Left) + sumOfLeftLeaves(root.Right)
}
// 为了符合本题要求,改造一下
func isTreeNode(root *TreeNode) bool {
return root.Right == nil && root.Left == nil
}
func sumOfLeftLeaves(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
var left int
if root.Left != nil && isTreeNode(root.Left) {
left = root.Left.Val
}
return left + sumOfLeftLeaves(root.Left) + sumOfLeftLeaves(root.Right)
}不过看了题解,比较麻烦,竟然直接上 dfs 了,这里贴一下官方的解法:
func isLeafNode(node *TreeNode) bool {
return node.Left == nil && node.Right == nil
}
func dfs(node *TreeNode) (ans int) {
if node.Left != nil {
if isLeafNode(node.Left) {
ans += node.Left.Val
} else {
ans += dfs(node.Left)
}
}
if node.Right != nil && !isLeafNode(node.Right) {
ans += dfs(node.Right)
}
return
}
func sumOfLeftLeaves(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
return dfs(root)
}No.437 路径总和 III
给定一个二叉树的根节点
root,和一个整数targetSum,求该二叉树里节点值之和等于targetSum的 路径 的数目。路径 不需要从根节点开始,也不需要在叶子节点结束,但是路径方向必须是向下的(只能从父节点到子节点)。
package main
type TreeNode struct {
Val int
Left *TreeNode
Right *TreeNode
}
// result 存储最终的路径数量
var result int
// prefixSumMap 存储前缀和及其出现次数
// key: 前缀和, value: 出现次数
var prefixSumMap map[int]int
func pathSum(root *TreeNode, targetSum int) int {
result = 0
prefixSumMap = make(map[int]int)
// 初始前缀和为0,出现次数为1,为了处理从根节点开始的路径
prefixSumMap[0] = 1
dfs(root, 0, targetSum)
return result
}
// dfs 深度优先搜索函数
// node: 当前节点
// currentSum: 从根节点到当前节点的前缀和
// targetSum: 目标和
func dfs(node *TreeNode, currentSum int, targetSum int) {
if node == nil {
return
}
// 1. 更新当前前缀和
currentSum += node.Val
// 2. 检查是否存在目标路径
// 如果 map 中存在 currentSum - targetSum,说明找到了一条路径
if count, ok := prefixSumMap[currentSum-targetSum]; ok {
result += count
}
// 3. 将当前前缀和存入 map
prefixSumMap[currentSum]++
// 4. 递归遍历左右子树
dfs(node.Left, currentSum, targetSum)
dfs(node.Right, currentSum, targetSum)
// 5. 回溯:移除当前前缀和,避免影响其他分支
// 遍历完当前节点的所有子节点后,需要将当前前缀和的计数减1,
// 以便在向上回溯时,不影响到其他分支的计算
prefixSumMap[currentSum]--
}No.543 二叉树的直径
给你一棵二叉树的根节点,返回该树的 直径 。
二叉树的 直径 是指树中任意两个节点之间最长路径的 长度 。这条路径可能经过也可能不经过根节点
root。两节点之间路径的 长度 由它们之间边数表示。
package main
import "math"
// TreeNode 定义了二叉树节点
type TreeNode struct {
Val int
Left *TreeNode
Right *TreeNode
}
// 使用一个全局变量来跟踪遇到的最大直径
var maxDiameter int
func diameterOfBinaryTree(root *TreeNode) int {
// 初始化最大直径为0
maxDiameter = 0
dfs(root)
return maxDiameter
}
// dfs 辅助函数,返回以当前节点为根的最大深度
func dfs(node *TreeNode) int {
// 1. 基准情况
if node == nil {
return 0
}
// 2. 递归计算左右子树的深度
leftDepth := dfs(node.Left)
rightDepth := dfs(node.Right)
// 3. 更新最大直径
// 以当前节点为根的直径是左子树深度 + 右子树深度
currentDiameter := leftDepth + rightDepth
if currentDiameter > maxDiameter {
maxDiameter = currentDiameter
}
// 4. 返回当前节点的最大深度,用于父节点的计算
// 深度是左右子树最大深度 + 1
return int(math.Max(float64(leftDepth), float64(rightDepth))) + 1
}No.563 二叉树的坡度
- 链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-tilt/
- 思路:深度优先搜索,在遍历每个结点时,累加其左子树和右子树结点之和的差的绝对值。而左子树之和也是左边所有节点坡度之和。
一个树的 节点的坡度 定义即为,该节点左子树的节点之和和右子树节点之和的 差的绝对值 。如果没有左子树的话,左子树的节点之和为 0 ;没有右子树的话也是一样。空结点的坡度是 0 。
func abs(a,b int) int {
if a-b > 0 {
return a-b
} else {
return b-a
}
}
func findTilt(root *TreeNode) (ans int) {
var dfs func(*TreeNode) int
dfs = func(node *TreeNode) int {
if node == nil {
return 0
}
sumLeft := dfs(node.Left)
sumRight := dfs(node.Right)
ans += abs(sumLeft,sumRight)
return sumLeft + sumRight + node.Val
}
dfs(root)
return
}No.637 二叉树的层平均值
- 链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/average-of-levels-in-binary-tree/
- 思路:还以为是计算所有层,取个平均值,没想到是个最简单的 bfs… ,好吧,就当重新练习 bfs 了。
func averageOfLevels(root *TreeNode) []float64 {
var res []float64
if root == nil {
return res
}
queue := list.New()
queue.PushFront(root)
for queue.Len() > 0 {
queueLength := queue.Len()
levelSum := 0
for i := 0 ; i < queueLength ; i ++ {
node := queue.Remove(queue.Front()).(*TreeNode)
if node.Left != nil {
queue.PushBack(node.Left)
}
if node.Right != nil {
queue.PushBack(node.Right)
}
levelSum += node.Val
}
if queueLength != 0 {
res = append(res, float64(levelSum/queueLength))
}
}
return res
}No.662 二叉树的最大宽度
- 链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-width-of-binary-tree/
- 思路:如何计算宽度是关键,记住不是计算一层的元素,而是计算宽度!!!
记root节点位置为1。可以发现左节点位置是父节点位置x2 - 1,右节点位置是父节点位置x 2,最后将每层最右边的位置-最左边的位置+1即是该层的层宽
func widthOfBinaryTree(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
queue := list.New()
queue.PushFront(root)
var maxWidth int // 记录最大宽度
NodeTreeLocation := make(map[*TreeNode]int) // 记录每一个节点的位置信息
for queue.Len() != 0 {
length := queue.Len()
curLevelMin := NodeTreeLocation[queue.Front().Value.(*TreeNode)] // 当前层最左节点位置(默认第一个)
curLevelMax := NodeTreeLocation[queue.Front().Value.(*TreeNode)] // 当前层最右节点位置(默认第一个)
for i := 0; i < length ; i ++ {
cur := queue.Remove(queue.Back()).(*TreeNode)
node := NodeTreeLocation[cur] // 父节点的位置
if node > curLevelMax { // 寻找当前层的最大节点
curLevelMax = node
}
if node < curLevelMin {
curLevelMin = node
}
if cur.Left != nil { // 对下一层节点位置进行赋值
queue.PushFront(cur.Left)
NodeTreeLocation[cur.Left] = node * 2 - 1
}
if cur.Right != nil {
queue.PushFront(cur.Right)
NodeTreeLocation[cur.Right] = node * 2
}
}
if maxWidth < (curLevelMax - curLevelMin) + 1 {
maxWidth = (curLevelMax - curLevelMin) + 1
}
}
return maxWidth
}